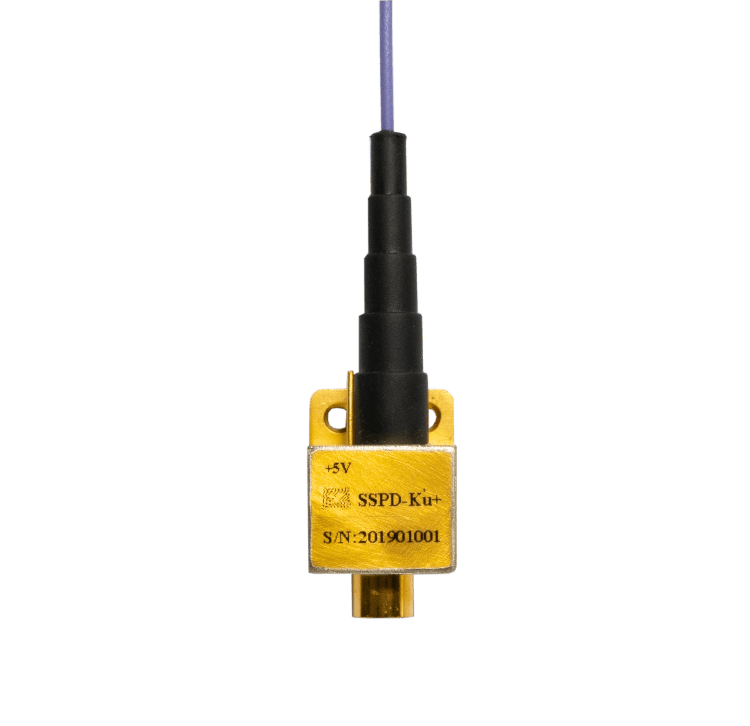
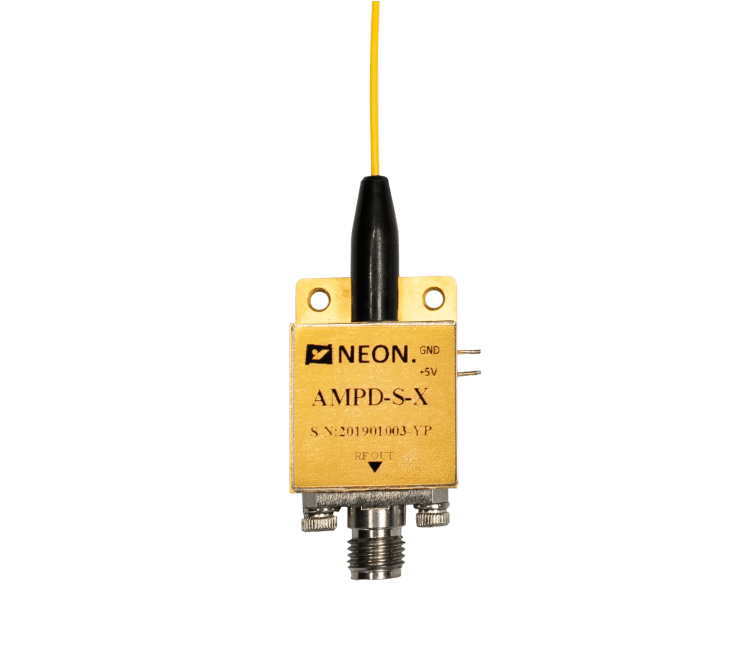
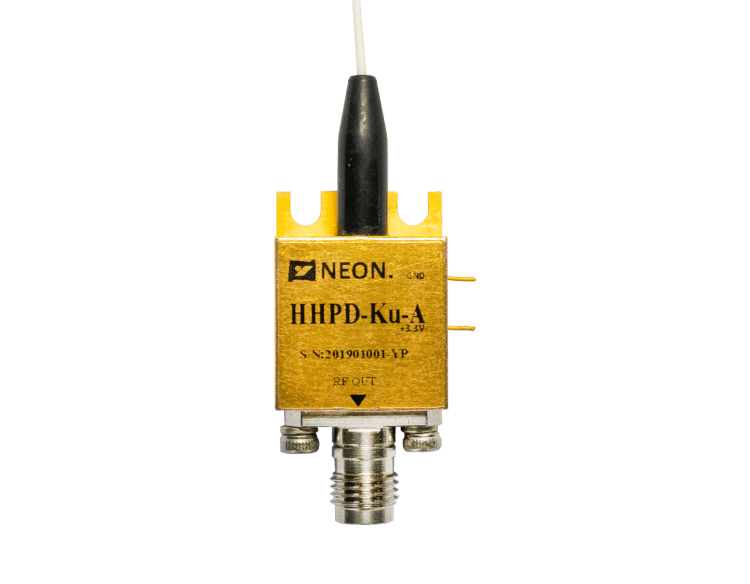
How to Choose the Right InGaAs Optical Photodetector?
InGaAs optical photodetectors are highly sensitive devices that are widely used in a range of applications such as telecommunications, remote sensing, and spectroscopy. They are capable of detecting light in the near-infrared (NIR) region of the electromagnetic spectrum, which is essential for many applications. However, selecting the right InGaAs photodetector for your specific needs can be a daunting task, considering the numerous parameters and specifications that need to be taken into account. In this article, we will guide you through the process of selecting the right InGaAs optical photodetector for your application.
Understanding InGaAs Optical Photodetectors
InGaAs photodetectors are made from a material called indium gallium arsenide, which is a semiconductor material with a bandgap that corresponds to the NIR region of the electromagnetic spectrum. When light enters the detector, it generates an electron-hole pair that can be measured as a current. InGaAs photodetectors are highly sensitive and can detect low levels of light with high accuracy.
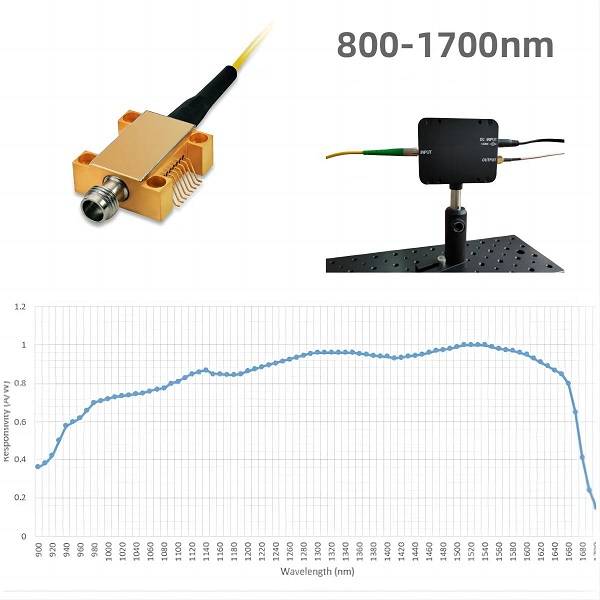
The advantages of InGaAs photodetectors are their high sensitivity, high quantum efficiency, and low noise level. InGaAs detectors can detect light in the 800nm to 1700nm wavelength range, making them suitable for a range of applications.
Key Parameters to Consider
When selecting an InGaAs photodetector, there are several key parameters to consider. These parameters will depend on the specific application, and it is important to understand the significance of each parameter and how it may impact the performance of the photodetector.
Wavelength Range: InGaAs photodetectors are sensitive to wavelengths in the near-infrared (NIR) range, typically from 800 to 1700 nm. The specific wavelength range required for your application will depend on the nature of the optical signal being detected. It is important to select a photodetector with a wavelength range that is appropriate for your application.
Sensitivity: The sensitivity of an InGaAs photodetector is a measure of how effectively it converts incident optical power into an electrical signal. Sensitivity is typically expressed in units of amps per watt (A/W), and a higher sensitivity of the InGaAs sensor means that the photodetector can detect weaker optical signals. When selecting a photodetector, it is important to consider the sensitivity required for your application and select a photodetector with a sensitivity that is appropriate.
Noise Level: The noise level of an InGaAs photodetector is a measure of the electrical noise that is present in the output signal. The noise level can impact the accuracy and precision of the measurements obtained with the photodetector. When selecting a photodetector, it is important to consider the noise level and select a photodetector with a noise level that is appropriate for your application.
Response Time: The response time of an InGaAs photodetector is a measure of how quickly it can detect changes in incident optical power. Response time is typically expressed in units of nanoseconds (ns), and a faster response time means that the photodetector can detect rapid changes in optical power. When selecting a photodetector, it is important to consider the response time required for your application and select a photodetector with a response time that is appropriate.
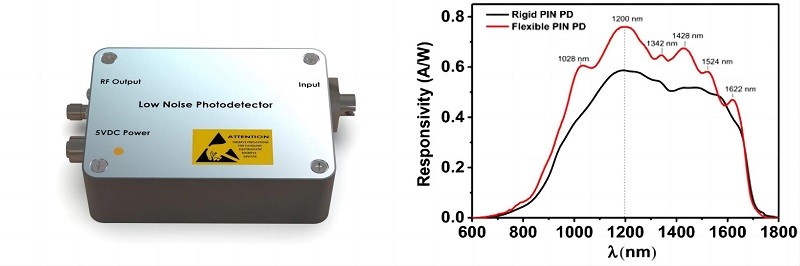
Spectral Response Linearity: The spectral response linearity of an InGaAs photodetector is a measure of how accurately it can detect optical signals across its wavelength range. Spectral response linearity can impact the accuracy of the measurements obtained with the photodetector. When selecting a photodetector, it is important to consider the spectral response linearity and select a photodetector with a spectral response that is appropriate for your application.
Packaging and Interfaces: InGaAs photodetectors are available in a range of packages and with different interfaces. It is important to select a photodetector with a package and interface that is appropriate for your application. Common packages include TO-can, pigtail, and butterfly, while common interfaces include SMA, FC, and LC.
Cost: The cost of an InGaAs photodetector can vary depending on its performance characteristics and packaging. It is important to consider the cost of the photodetector and select a photodetector that is within your budget while meeting the required performance for your application.
Choosing the Right InGaAs Photodetector: A Step-by-Step Guide
Choosing the right InGaAs photodetector can be a challenging process. However, by following a step-by-step approach, you can ensure that you select a photodetector that meets your application requirements and performs reliably over the long term. Here is a step-by-step guide to choosing the right InGaAs photodetector:
Define Your Application Requirements: The first step in selecting an InGaAs photodetector is to define your application requirements. This includes the wavelength range of interest, the sensitivity required, the level of noise tolerance, the required response time, and any other critical parameters.
Identify the Critical Parameters: Once you have defined your application requirements, it is important to identify the critical parameters for your specific application. These parameters may vary depending on the nature of your application, but they typically include wavelength range, sensitivity, noise level, response time, spectral response linearity, packaging and interfaces, and cost.
Compare and Evaluate Different Options: After identifying the critical parameters, you can begin to compare and evaluate different InGaAs photodetector options. Look for photodetectors that meet your critical parameters and compare their performance characteristics, packaging options, and interfaces. Consider the cost of the photodetector, as well as any long-term maintenance and reliability concerns.
Consult with Experts and Manufacturers: It is important to consult with experts and manufacturers during the selection process. They can provide valuable guidance and support in selecting the right InGaAs photodetector for your application. They can also provide information about the latest advances in InGaAs photodetector technology and help you stay up-to-date with the latest trends and developments.
Consider Long-Term Maintenance and Reliability: When selecting an InGaAs photodetector, it is important to consider long-term maintenance and reliability. Look for photodetectors that are designed for reliability and that require minimal maintenance over their lifetime. Consider the manufacturer’s warranty and technical support options to ensure you have the necessary support in case of any issues or problems.

By following these steps, you can select the right InGaAs photodetector for your specific application. Remember to take the time to carefully evaluate different options and consult with experts and manufacturers to ensure that you select a photodetector that meets your needs and performs reliably over the long term.
In summary, selecting the right InGaAs optical photodetector requires careful consideration of key parameters such as wavelength range, sensitivity, noise level, response time, spectral response linearity, packaging and interfaces, and cost. By taking these parameters into account and consulting with experts in the field, you can select the right photodetector for your specific needs, ensuring accurate and reliable measurements. InGaAs photodetectors are powerful tools that can enable a range of applications in telecommunications, remote sensing, and spectroscopy, and selecting the right photodetector is critical to the success of these applications.